What Is a Damp Proof Course (DPC) and Why Is It Important?
A Damp Proof Course (DPC) is a protective barrier that prevents moisture from the ground from rising up into the property. Installing an effective DPC is crucial for keeping a home free of damp and mould. This article will explain what a DPC is, the history of DPCs in the UK, why they are important, the different types available, and how they can fail.
What is a Damp Proof Course?
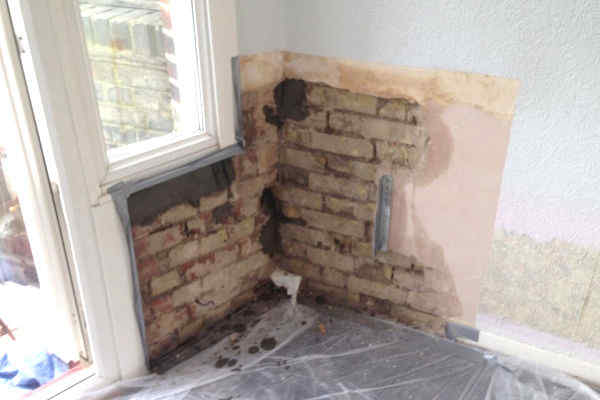
A DPC is a horizontal barrier made from waterproof material that is inserted into walls 150mm above ground level. It blocks moisture from the soil outside from being absorbed into the porous material of the walls, such as brick or stone. This stops damp from climbing up inside the walls via capillary action.
Without a DPC, moisture could enter the property, causing issues like damp walls, mould growth, rotting skirting boards and structural damage.
History of DPCs in the UK
The origins of DPCs in the UK can be traced back to the early 1900s, when various materials like lead, asphalt and bitumen were used. However, they only started becoming widespread in the 1950s.
Initially slate was a popular choice of DPC, but this rigid material can crack over time as the building settles, causing damp issues. Nowadays plastic DPC membranes made of materials like polyethylene are common.
The invention of cavity walls in the 1920s also helped combat rising damp, as the gap between the inner and outer wall acts as a barrier.
Why are DPCs Important?
Installing an effective DPC is vital for protecting buildings against damp and water damage. Here are some key reasons they are essential:
- Prevents rising damp – Stops ground moisture climbing up walls via capillary action through porous materials like brick. This stops internal walls becoming damp.
- Reduces risk of rot and wood damage – Dampness causes wood to decay, so a DPC protects critical structural timbers.
- Avoids mould growth – Excess moisture enables mould to grow on walls and ceilings, which can cause health issues. A DPC prevents this.
- Stops musty odours – Dampness leads to unpleasant musty smells in a property. An effective DPC blocks this moisture to avoid this.
- Protects decoration – Water damage can ruin wallpaper, paint and plaster. A properly installed DPC prevents decor from being spoiled.
- Maintains structural integrity – Damp weakens walls long-term, but a DPC protects the stability and strength of the building.
Types of DPC
There are several types of damp proof course available:
Plastic DPC Membrane
Modern DPCs are typically made using a thin, flexible plastic membrane. Polyethylene is commonly used as it is an effective water barrier. These plastic DPCs are installed during construction of new builds.
Chemical DPC Injection
This involves drilling small holes into the mortar course directly above ground level and injecting a silicone-based liquid damp-proofing cream. This then reacts to form a water-repellent barrier.
Cavity Wall DPC
In cavity wall construction, the gap between the inner and outer wall itself acts as a moisture barrier. No separate DPC membrane is installed.
Concrete Floor DPC
A polythene sheet can be laid underneath a ground floor concrete slab to prevent moisture rising up from the soil underneath.
When properly installed and maintained, a DPC prevents a wide range of problems related to dampness and water ingress. This helps maintain the structural integrity of the property as well as creating a healthier indoor environment.